Head Protection-Hard Hats
Over 70,000 disabling head injuries occur every year in industry. Hard-hats were worn by only 16% of workers who sustained head injuries.
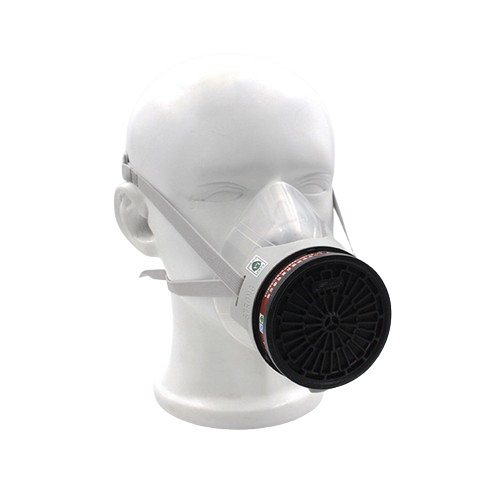
Head protection, in the form of protective hats must do two things: resist penetration and be shock absorbent.
This is accomplished by making the shell of the hat of a material hard enough to resist the blow and utilizing a shock absorbing lining composed of a headband and crown straps to keep the shell away from the wearer's skull. This is sometimes called the suspension system.

In order to provide maximum protection, there must be at least one inch of clearance between the shell and the skull. If the protective hat is not worn correctly, such as backwards, this clearance is negated and your level of protection is compromised. Protective hats are also used to protect against electrical shock, their design and materials of construction are created to resist electrical current and act as an electrical insulator. Each type and class of head protection is intended to provide protection against specific hazardous conditions. Your understanding of these conditions will help in selecting the right half for the particular situation.
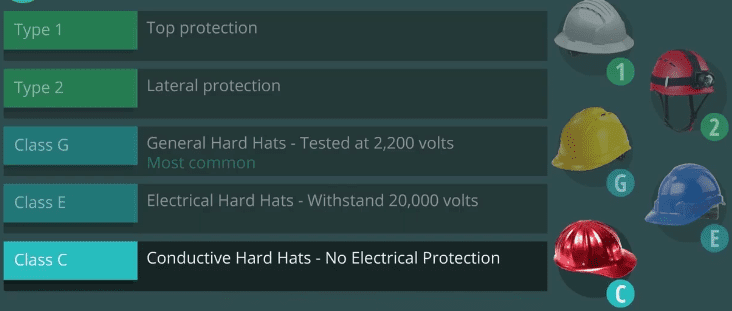
Protective hats are classified in two types and three classes. Type one hats are for top protection and have a full brim not less than one and one quarter inches wide. Type two are designed for lateral impact protection and are brimless.
The three classes indicate the helmet's electrical insulation rating, class G for general hard hats are tested at 2200 volts. They are the most common class used in industry for protection against impact hazards. Class E for electrical hard hats are tested to withstand 20,000 volts and are considered a utility service hat that are usually used for protection of electrical workers from high voltage as well as impact. Class C for conductive hard hats provide no electrical protection. Class C hard hats are designed for lightweight comfort and impact protection. They are usually made of aluminum and provide no protection from electrical current contact. Class C hard hats are generally used in certain manufacturing, or construction occupations where there is no danger from electrical shock.
ANSl recently updated the hard hat classifications. Your organization may still have some hard hats on site with old classes. The previous classifications were A, general hard hats, B, electrical hard hats, and C hard hats stayed the same. You can identify the type and class of a hard hat by looking for the manufacturer's label inside the shell. This label must have the ANSI.Z891 designation meaning it meets the standards of the type and class designated.










